Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM): A Definitive Guide
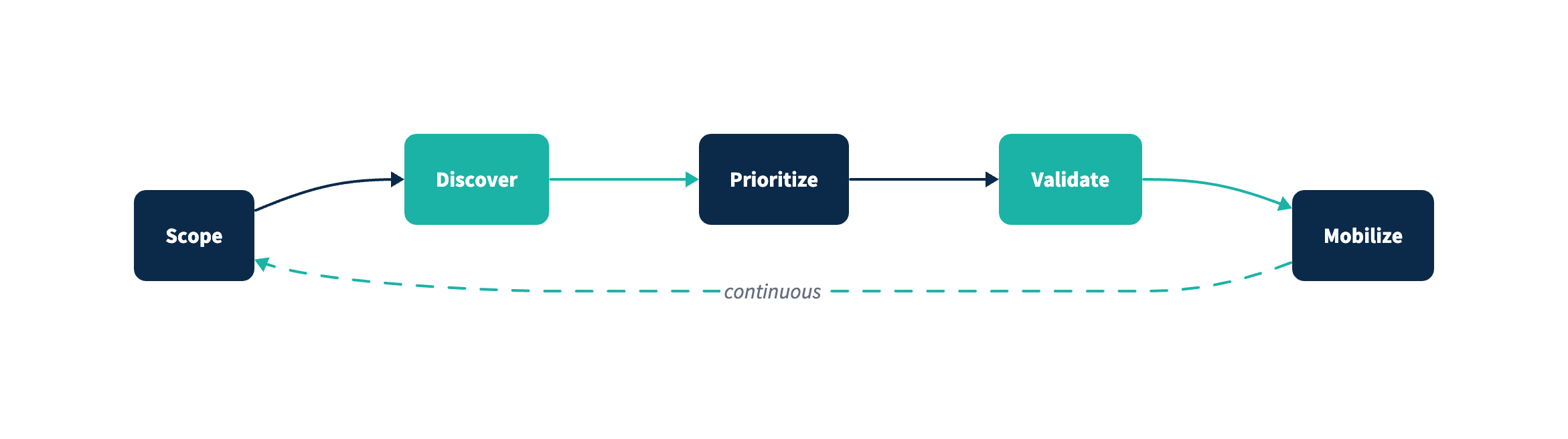
CTEM in one sentence: Continuous Threat Exposure Management is Gartner's five-stage cycle (Scoping, Discovery, Prioritization, Validation, Mobilization) for systematically reducing real-world security exposure.
CTEM.org in one sentence: An open standard of CTEM identifiers (CTEM-IDs)—like CVE numbers but for exposure types—plus a machine-readable JSON feed.
In today's dynamic cyber threat landscape, organizations face an ever-evolving array of vulnerabilities and attack vectors. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), a concept introduced by Gartner, offers a proactive and structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks in real time. By continuously monitoring and refining security postures, CTEM enables businesses to stay ahead of potential threats.
What is CTEM?
CTEM is a framework designed to reduce an organization's exposure to cyber threats by:
- Continuously identifying vulnerabilities and attack paths.
- Prioritizing risks based on their potential impact on critical assets.
- Validating security measures to ensure effectiveness.
- Systematically remediating threats in a coordinated and iterative manner.
Unlike traditional security programs that focus on periodic assessments, CTEM operates as a continuous cycle, ensuring that organizations remain resilient against emerging threats.
The Five Stages of CTEM
1. Scoping
The foundation of any CTEM program begins with scoping. This involves:
- Identifying critical assets and their importance to the business.
- Understanding the organization's attack surface, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Defining key objectives and metrics for success.
2. Discovery
In this stage, organizations map out their entire ecosystem to uncover vulnerabilities and exposures. This phase highlights the importance of robust tooling for discovering assets, misconfigurations, and vulnerabilities. However, these tools alone are not enough. Substantial human effort is required to classify findings, correlate them with business context, and prioritize them effectively. Key activities include:
- Conducting asset inventories.
- Performing vulnerability assessments.
- Identifying misconfigurations and identity risks.
- Mapping potential attack paths.
3. Prioritization
Given the sheer volume of exposures, prioritization is critical. This stage focuses on:
- Ranking risks based on factors like exploitability, business impact, and existing security controls.
- Using a threat-centric approach to address the most critical vulnerabilities first.
4. Validation
Validation ensures that identified threats are actionable and that security controls can mitigate them effectively. Techniques include:
- Simulating attacks through red teaming or penetration testing.
- Testing response plans and mitigation strategies.
- Verifying the effectiveness of implemented controls.
5. Mobilization
The final stage focuses on executing remediation efforts and tracking progress. Key actions include:
- Coordinating between security and IT teams to address prioritized threats.
- Implementing patches, configuration updates, or new security controls.
- Monitoring improvements to ensure continuous progress.
Why CTEM Matters
With digital transformation accelerating, organizations' attack surfaces are growing larger and more complex. Traditional reactive measures are no longer sufficient to manage modern threats. CTEM provides:
- Proactive Risk Management: Addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Real-Time Visibility: Continuous monitoring of the organization's security posture.
- Improved Decision-Making: Actionable insights that align security efforts with business goals.
- Cost Efficiency: Reducing the financial and reputational impact of breaches by preventing them.
Common Challenges in Implementing CTEM
While the benefits of CTEM are clear, organizations often face challenges such as:
- Balancing Automation with Human Effort: Tools are essential for discovery and management, but significant manual effort is needed to interpret findings, classify threats, and coordinate effective responses.
- Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and skilled personnel.
- Integration Complexity: Incorporating CTEM into existing security infrastructures.
- Overwhelming Volume of Vulnerabilities: Managing the sheer number of potential exposures.
Addressing these hurdles requires a strategic approach and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Best Practices for CTEM Implementation
- Align with Business Objectives: Ensure that CTEM efforts support overarching business goals.
- Leverage Automation: Use tools and technologies to streamline processes while retaining human oversight.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage cross-functional collaboration between security, IT, and other stakeholders.
- Iterate and Improve: Regularly review and refine CTEM processes to adapt to emerging threats.
The Future of CTEM
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, CTEM will continue to play a pivotal role in helping organizations achieve resilience. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enhance threat detection and response capabilities. Furthermore, deeper integration with frameworks like Zero Trust will enable more adaptive and effective security strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CTEM?
CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management) is Gartner's five-stage framework for systematically reducing security exposure: Scoping, Discovery, Prioritization, Validation, and Mobilization. Unlike periodic assessments, CTEM operates as a continuous cycle.
What are the 5 stages of CTEM?
The five stages are: 1) Scoping - defining what matters to protect, 2) Discovery - finding vulnerabilities and exposures, 3) Prioritization - ranking risks by business impact, 4) Validation - testing that controls work, 5) Mobilization - coordinating remediation.
How is CTEM different from vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management focuses on software flaws (CVEs). CTEM is broader—it covers any exposure that puts data, identity, or infrastructure at risk: credential leaks, lookalike domains, misconfigurations, infected devices, and more.
What are CTEM Identifiers?
CTEM Identifiers (CTEM-IDs) are standardized labels for security exposures, similar to how CVE numbers identify vulnerabilities. CTEM.org maintains an open catalog of these identifiers with a machine-readable JSON feed at ctem.org/source.json.
Join CTEM.org and Stay Ahead of the Curve
Joining our group CTEM.org is a unique opportunity to help shape the future of this evolving standard or stay up to date on the latest trends and vendors in the space.
As a member, you can contribute to the development of best practices, stay informed about the latest strategies and technologies, and collaborate with peers who are leading the charge in proactive cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Continuous Threat Exposure Management represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity.
By adopting a proactive, continuous approach, organizations can better protect their critical assets, reduce their attack surfaces, and align security efforts with business objectives. Whether you're just starting your CTEM journey or looking to refine an existing program, embracing this framework is essential for staying ahead in today's threat landscape.